
What is Wi-Fi HaLow-802.11ah?Tuya WIFI HaLow IP Camera
Wi-Fi HaLow is coming to smart door locks, thermostats, security cameras, wearables, electronic shelf labels and wireless sensor networks all around you. It is the main networking mode for future 5G and 6G smart home products. What is Wi-Fi HaLow, and what makes it the ideal wireless protocol for future Internet of Things (IoT) connections? What scenarios can Wi-Fi HaLow be applied in the future?

What is Wi-Fi HaLow?
Traditional Wi-Fi is the most ubiquitous wireless network protocol in use today, carrying more than half of Internet traffic. The Wi-Fi Alliance has introduced Wi-Fi HaLow (pronounced HAY-Low), a new, low-power, long-range version of Wi-Fi designed to meet the unique requirements of the Internet of Things. Based on the IEEE 802.11ah standard, Wi-Fi HaLow builds on the market success of Wi-Fi to deliver a no-compromise wireless solution that delivers the energy efficiency, extended range, obstacle penetration, Native IP support, ease of use and state-of-the-art security features.
Wi-Fi HaLow builds on the market success of Wi-Fi to increase the range and battery life of Wi-Fi connected devices. Wi-Fi HaLow also meets the scalability, robustness and security requirements needed to handle the most challenging IoT environments. While there is no "one size fits all" wireless protocol for all IoT scenarios, Wi-Fi HaLow is the first to address the most pressing needs of IoT applications, making it ideal for our connected world. The list of applications for Wi-Fi HaLow ranges from wireless sensors, actuators and security cameras to door locks, appliances and thermostats, all designed to improve the user experience and productivity while reducing installation and operating costs.
Advantages of Wi-Fi HaLow
Traditional Wi-Fi enables end users to quickly stream movies and download files on various radio frequencies in the 2.4GHz, 5GHz and 6GHz bands. These higher frequency Wi-Fi connections have short range and drain batteries quickly, requiring frequent recharging, battery replacement, or plugging. For example, while Wi-Fi 6 is ideal for bandwidth-intensive applications like 4K video streaming and augmented reality, it's not a good choice for connected devices that must run on batteries for extended periods of time.
The high power consumption, distance limitations and traffic congestion of traditional Wi-Fi networks, as well as the limited number of devices that can be connected to a single wireless access point (AP), are no longer feasible in the connected world of smart devices. This limitation is holding back new IoT-centric business models emerging across industries that require greater capacity, range and endurance, as well as lower deployment costs and shorter installation times.
Wi-Fi HaLow is designed to reduce power consumption, increase wireless range and data rates without limiting performance, and support more devices on the network. By leveraging new power-saving sleep modes, Wi-Fi HaLow enables new types of IoT products that can run on batteries for years while still delivering many Mbps of data throughput. Wi-Fi HaLow is ideal for massive IoT as it can support more than 8,000 connections from a single access point.
Wi-Fi HaLow builds on the strong security and spectrally efficient OFDM of traditional Wi-Fi, while using narrower radio frequency channels below 1GHz to better penetrate obstacles. By operating in the sub-GHz range, Wi-Fi HaLow also avoids the highly congested 2.4GHz band.

Extending the Reach of IoT Connectivity
The 802.11 standard covers an unusually wide range of frequencies, from sub-gigahertz (GHz) to millimeter wave (mmWave). Wi-Fi HaLow is the first Wi-Fi standard to operate in the unlicensed sub-1 GHz band. General rule: the lower the frequency, the wider the coverage and the better the ability to penetrate obstacles. As a sub-1 GHz protocol, Wi-Fi HaLow signals pass through walls and other obstacles more easily than 2.4GHz options. In addition, Wi-Fi HaLow uses a narrower frequency band, one-tenth that of traditional Wi-Fi. The combination of sub-1 GHz frequencies and narrower frequency bands allows W-Fi HaLow devices to reach 10 times the distance, cover 100 times the area, and support 1,000 times the capacity with a single access point while more easily overcoming signal obstacle.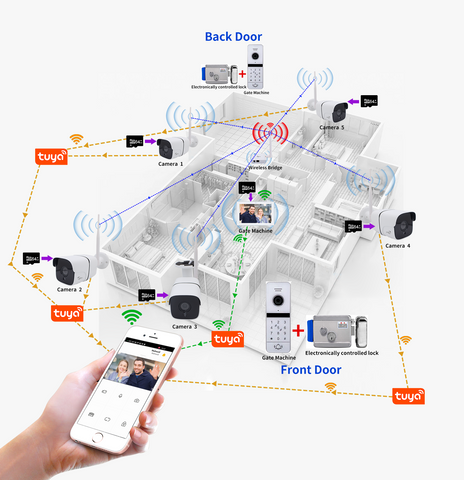
With its long-range coverage of sub-1 GHz signals, Wi-Fi HaLow has the benefit of extending the range of smart home or smart city networks, allowing users to control IoT devices up to 1 km away. This is well beyond the range of other short-range protocols like Bluetooth, Zigbee or Z-Wave. While mobile IoT technologies such as LTE-M and NB-IoT enable long-range connectivity, they use licensed spectrum, requiring end users to pay for potentially expensive data plans. Other long-range wireless networks, such as LoRa and Sigfox, have very low data rates for small packets, while Wi-Fi HaLow has data rates ranging from hundreds of Kb/s to tens of Mb/s, making it an ideal solution for expanding IoT coverage The best choice for the range.
A single Wi-Fi HaLow access point can also cover thousands of connected devices in a star network, bypassing complex, difficult-to-deploy and bandwidth-constrained mesh networks, simplifying network installation and minimizing total ownership cost.
A power-saving protocol
The Wi-Fi HaLow protocol provides superior energy efficiency for power-sensitive IoT devices that often sleep for long periods of time. This enables flexible power and battery options, from short-range IoT devices running on coin cell batteries, to higher power, larger battery applications extending up to 1 km. Wi-Fi HaLow's sub-1 GHz narrowband signal travels farther, consumes less power, and can transmit more data per unit of energy than wireless options in the 2.4GHz band.

Wi-Fi HaLow supports new sleep and power management modes to enable longer battery life for IoT devices. Additionally, when combined with Morse Microelectronics' proprietary circuit design optimizations, Wi-Fi HaLow provides low-altitude power consumption comparable to many other wireless technologies.
All IoT networks require Internet Protocol (IP) support for cloud connectivity. Because Wi-Fi HaLow is an 802.11 Wi-Fi standard, it provides native TCP/IP support. Unlike other short-range protocol options such as Bluetooth or Zigbee, this built-in IP capability means there is no need for proprietary gateways or bridges to connect to the cloud for software updates or IoT application management.

Like other IEEE 802.11 Wi-Fi versions, Wi-Fi HaLow is itself a secure wireless protocol. Adopt the latest Wi-Fi Protected Access 3 (WPA3) security protocol, as well as encrypted information and unique ID technology for secure boot implementation. The high data rate of Wi-Fi HaLow also supports secure over-the-air (OTA) firmware upgrades while accelerating cloud connections. Since Wi-Fi HaLow is part of the IEEE 802.11 standard, Wi-Fi HaLow networks can also coexist with Wi-Fi 4, Wi-Fi 5, and Wi-Fi 6 networks without affecting their RF performance.

Application of Wi-Fi HaLow
Wi-Fi HaLow stands out for its versatility. Wi-Fi HaLow addresses a wide range of IoT use cases in smart homes, building automation, smart cities, and industrial and agricultural environments. Many applications, including process control sensors, building and industrial automation, warehouses and retail stores, will benefit from Wi-Fi HaLow technology, keeping many remote, power-sensitive devices connected in an increasingly automated world.
In the initial phase of deployment, Wi-Fi HaLow is expected to be used in indoor and outdoor applications that standard Wi-Fi cannot reach, such as battery-operated surveillance systems, wireless cameras and motion sensors. Large venues, such as concert halls, shopping malls, warehouses, hotels, and stadiums, are another use case where a single Wi-Fi HaLow access point can replace a large number of access points, avoiding the need to implement complex mesh networks over a limited area needs.
Potential use cases for Wi-Fi HaLow networks span IoT:
1. Smart Home Devices
2. Monitoring system
3. Access control
4. Industrial process control
5. Logistics and asset management
6. Retail labels, signs and scanners
7. Building automation
8. Wearables and mobile devices
9. Smart city infrastructure
10. Agricultural and environmental sensors
IoT devices with Wi-Fi HaLow will offer new options in the license-exempt sub-1 GHz band to support IP networks and OFDM modulation schemes widely used in the PC ecosystem. In the long run, Wi-Fi HaLow can be used to expand the range of applications for mobile devices, PCs, and IoT networks.





2 comments
unfriendly set up how do you view on pc very confusing no info thats useful
Noticed the board has terminals for possible radio connections. We’d be interested in more details in regards to baud rate and other specification of the board. We have possible applications for commercial irrigation systems here in the U.S. as we work with various manufacturers like Rain Bird, Toro and others.